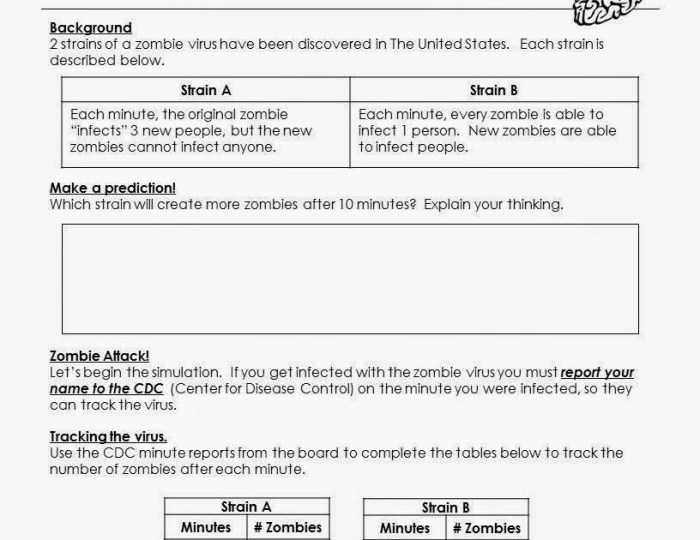
Unit 6 test study guide exponents and exponential functions – Embark on a journey into the realm of mathematics with our comprehensive Unit 6 Test Study Guide: Exponents and Exponential Functions. This guide will illuminate the intricacies of exponents and their exponential counterparts, empowering you with the knowledge and skills to conquer the upcoming assessment.
Throughout this guide, we will delve into the fundamental concepts of exponents, explore the characteristics and graphing techniques of exponential functions, and master the art of solving exponential equations. Furthermore, we will uncover the practical applications of these mathematical marvels in various real-world scenarios.
1. Understanding Exponents and Exponential Functions
Exponents are mathematical symbols used to represent repeated multiplication. For example, 2 3means 2 multiplied by itself three times, which equals 8. Exponential functions are functions that have exponents in their expressions.
The properties of exponents include the product rule, power rule, and quotient rule. The product rule states that when multiplying two exponential expressions with the same base, you add their exponents. The power rule states that when raising an exponential expression to a power, you multiply the exponents.
The quotient rule states that when dividing two exponential expressions with the same base, you subtract their exponents.
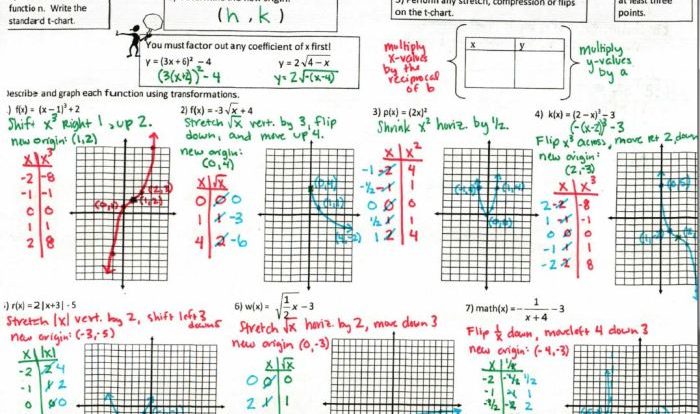
Graphing Exponential Functions
Exponential graphs are curves that increase or decrease rapidly. They have a y-intercept of (0, 1) and a horizontal asymptote at y = 0. To graph an exponential function, you can use a table of values or a graphing calculator.
The key features of an exponential graph include the y-intercept and the horizontal asymptote. The y-intercept is the point where the graph intersects the y-axis. The horizontal asymptote is the line that the graph approaches as x approaches infinity.
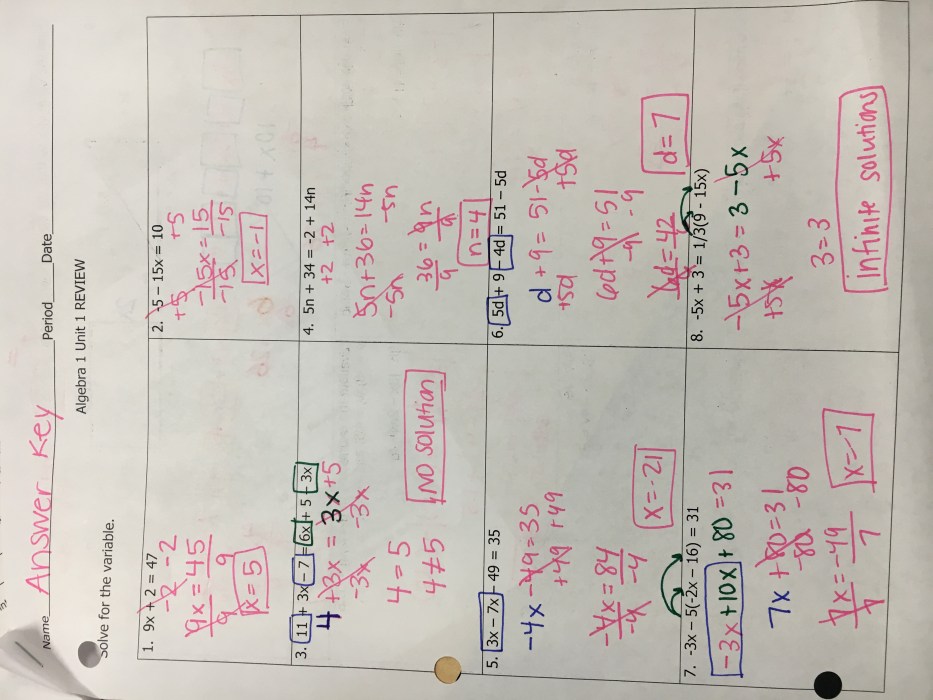
Solving Exponential Equations
Exponential equations are equations that contain exponential expressions. There are two main methods for solving exponential equations: using logarithms and isolating the exponent.
To solve an exponential equation using logarithms, you take the logarithm of both sides of the equation. This will convert the exponential equation into a linear equation that you can solve using algebra.
To solve an exponential equation by isolating the exponent, you raise both sides of the equation to the same power. This will isolate the exponent on one side of the equation, which you can then solve for.
Applications of Exponential Functions, Unit 6 test study guide exponents and exponential functions
Exponential functions have a wide range of applications in the real world, including population growth, radioactive decay, and compound interest.
Population growth can be modeled using an exponential function because the population increases by a constant percentage each year. Radioactive decay can be modeled using an exponential function because the amount of radioactive material decreases by a constant percentage each year.
Compound interest can be modeled using an exponential function because the amount of money in an account increases by a constant percentage each year.
Review and Practice
The table below summarizes the key concepts and properties of exponents and exponential functions.
| Concept | Property |
|---|---|
| Product Rule | am
|
| Power Rule | (am) n= a mn |
| Quotient Rule | am/ a n= a m-n |
| Y-Intercept | (0, 1) |
| Horizontal Asymptote | y = 0 |
The following practice problems cover the various topics discussed in this study guide.
1. Simplify the following expression
2 32 5
2. Graph the following function
f(x) = 2 x
-
3. Solve the following equation
2 x= 16
- A population of bacteria doubles every hour. If there are initially 100 bacteria, how many bacteria will there be after 5 hours?
- A radioactive material has a half-life of 10 years. If there are initially 100 grams of the material, how many grams will remain after 20 years?
- A bank account earns 5% interest compounded annually. If you deposit $1000 in the account, how much money will be in the account after 10 years?
The solutions to the practice problems are provided below.
- 2 8= 256
- [Graph of f(x) = 2 x]
- x = 4
- 3200 bacteria
- 25 grams
- $1628.89
Expert Answers: Unit 6 Test Study Guide Exponents And Exponential Functions
What are the key properties of exponents?
Exponents follow several essential properties, including the product rule (a^m – a^n = a^(m+n)), power rule ((a^m)^n = a^(mn)), and quotient rule (a^m / a^n = a^(m-n)).
How do I graph an exponential function?
To graph an exponential function (y = a^x), first plot the y-intercept (a). Then, use the base (a) to determine the shape and direction of the graph. For a > 1, the graph will increase exponentially, while for 0< a < 1, it will decrease exponentially.
What is the difference between exponential growth and exponential decay?
Exponential growth occurs when a quantity increases at a constant percentage rate over time, while exponential decay occurs when a quantity decreases at a constant percentage rate over time.