In the realm of mathematics education, Big Ideas Integrated Math 2 emerges as a beacon of innovation, igniting a passion for understanding the interconnectedness of mathematical concepts and their applications in the real world. This comprehensive curriculum invites students to delve into the depths of mathematical modeling, technology integration, and effective teaching strategies, empowering them to become critical thinkers and problem-solvers.
With a focus on developing students’ mathematical reasoning and problem-solving skills, Big Ideas Integrated Math 2 fosters a deep understanding of the fundamental concepts of algebra, geometry, statistics, and probability. Through engaging activities and real-world examples, students gain insights into the beauty and practicality of mathematics, fostering a lifelong appreciation for the subject.
Big Ideas in Integrated Math 2

In mathematics education, “big ideas” refer to fundamental concepts and principles that serve as the foundation for understanding and applying mathematics. Integrated Math 2 focuses on several key big ideas that provide a cohesive framework for exploring mathematical concepts and their connections to real-world applications.
The specific big ideas addressed in Integrated Math 2 include:
- Function: Functions are mathematical relationships that describe how one variable changes in response to another. They are essential for modeling real-world phenomena, such as the relationship between time and distance traveled.
- Change: Calculus, the branch of mathematics that deals with change, plays a significant role in Integrated Math 2. Students learn about rates of change, limits, and derivatives, which are used to analyze and predict how quantities change over time.
- Modeling: Mathematical modeling involves using mathematics to represent and solve real-world problems. Integrated Math 2 emphasizes the application of mathematical concepts to model and analyze various phenomena, such as population growth, projectile motion, and financial investments.
li> Probability and Statistics: Probability and statistics provide tools for analyzing and interpreting data. Integrated Math 2 introduces students to basic concepts of probability, sampling, and statistical inference, enabling them to make informed decisions based on data.
These big ideas are interconnected and build upon each other, providing a comprehensive understanding of mathematical concepts and their applications. For example, functions can be used to model change, and calculus provides tools for analyzing the rate of change. Probability and statistics can be used to analyze data and make predictions about future events.
Mathematical Modeling in Integrated Math 2
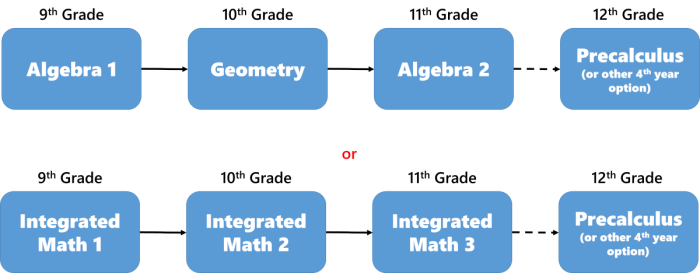
Mathematical modeling plays a pivotal role in Integrated Math 2, providing students with a powerful tool to solve problems and make predictions in various real-world contexts.
Students learn to construct mathematical models by translating real-world situations into mathematical equations or functions. These models represent the relationships between variables and can be used to predict outcomes, analyze data, and make informed decisions.
Examples of Mathematical Models in Integrated Math 2
- Linear Models:Students use linear models to represent relationships between two variables that change at a constant rate. These models can be used to predict values, such as the cost of a rental car based on the number of days rented.
- Exponential Models:Exponential models represent relationships where one variable grows or decays at a constant percentage rate. Students use these models to predict population growth, radioactive decay, and investment returns.
- Trigonometric Models:Trigonometric models describe periodic relationships, such as the motion of a pendulum or the height of a Ferris wheel. Students use these models to analyze wave patterns and solve problems involving angles and distances.
- Systems of Equations:Systems of equations model situations involving multiple variables and relationships. Students solve these systems to find values that satisfy all the equations simultaneously, helping them solve complex problems in various fields.
- Probability Models:Probability models predict the likelihood of events occurring. Students use these models to analyze data, make inferences, and make decisions based on probability.
Technology in Integrated Math 2
Technology plays a crucial role in Integrated Math 2, enhancing student learning and engagement. It allows students to visualize complex concepts, explore real-world applications, and develop problem-solving skills.
Use of Technology, Big ideas integrated math 2
Integrated Math 2 incorporates various technologies, including:
- Graphing calculators:Used for graphing functions, solving equations, and exploring data.
- Dynamic geometry software:Allows students to create and manipulate geometric figures, explore transformations, and test conjectures.
- Spreadsheets:Used for organizing and analyzing data, creating graphs, and modeling real-world situations.
- Computer algebra systems (CAS):Provide symbolic manipulation capabilities, such as solving equations, factoring polynomials, and simplifying expressions.
- Online simulations and applets:Engage students with interactive experiences, allowing them to explore mathematical concepts and real-world applications.
Assessment in Integrated Math 2

Assessment in Integrated Math 2 plays a crucial role in evaluating students’ understanding of mathematical concepts and their ability to apply them in real-world contexts. Various types of assessments are used to measure students’ progress and provide feedback to both students and teachers.
Formative Assessments
Formative assessments are designed to provide ongoing feedback during the learning process. They help identify areas where students need additional support and allow teachers to adjust their instruction accordingly. Examples of formative assessments include:
- Class discussions
- Quizzes
- Homework assignments
- Student self-reflections
Summative Assessments
Summative assessments are used to evaluate students’ overall understanding of a unit or course at the end of a learning period. They provide a snapshot of students’ achievement and help teachers determine grades. Examples of summative assessments include:
- End-of-chapter tests
- Midterm exams
- Final exams
- Projects
Effective Assessment Practices
Effective assessment practices in Integrated Math 2 include:
- Alignment with Learning Objectives:Assessments should be aligned with the learning objectives of the course to ensure that they measure what students are expected to learn.
- Variety of Assessment Types:Using a variety of assessment types allows teachers to assess different aspects of students’ understanding, such as conceptual understanding, problem-solving skills, and communication skills.
- Feedback and Reflection:Providing timely and specific feedback to students on their assessments helps them identify areas for improvement and reflect on their learning.
- Use of Technology:Technology can be integrated into assessments to enhance student engagement and provide real-time feedback.
Teaching Strategies for Integrated Math 2: Big Ideas Integrated Math 2

Integrated Math 2 combines algebraic, geometric, and statistical concepts to develop students’ mathematical understanding and problem-solving skills. Effective teaching strategies for this subject emphasize active learning, collaboration, and real-world applications.Creating a positive and supportive learning environment is crucial. This involves establishing clear expectations, fostering open communication, and valuing diverse perspectives.
Students should feel comfortable asking questions, sharing ideas, and collaborating with peers.
Instructional Strategies
Effective teaching strategies in Integrated Math 2 include:
-
-*Inquiry-based learning
Engage students in hands-on activities and investigations that encourage them to explore mathematical concepts and discover patterns.
-*Project-based learning
Assign projects that require students to apply mathematical concepts to solve real-world problems and develop their critical thinking skills.
-*Differentiated instruction
Tailor instruction to meet the needs of diverse learners by providing multiple pathways to understanding and assessment.
-*Technology integration
Use technology tools to enhance student engagement, provide interactive simulations, and facilitate data analysis.
Big Ideas Integrated Math 2 offers a wide range of engaging activities and problem-solving exercises. Take, for instance, the intriguing question: “Can you spell water in three letters?” Click here to find out the answer. Returning to our math exploration, Big Ideas Integrated Math 2 encourages students to think critically and develop a deep understanding of mathematical concepts.
-*Collaborative learning
Encourage students to work together in small groups to solve problems, share ideas, and learn from each other.
Assessment Strategies
Regular assessment is essential for monitoring student progress and providing feedback. Effective assessment strategies in Integrated Math 2 include:
-
-*Formative assessments
Use frequent quizzes, homework assignments, and class discussions to provide ongoing feedback and identify areas for improvement.
-*Summative assessments
Conduct unit tests, projects, and end-of-course exams to evaluate student mastery of mathematical concepts and problem-solving skills.
-*Self-assessment
Encourage students to reflect on their own understanding and progress through self-assessment activities.
By implementing these effective teaching strategies, educators can create a dynamic and engaging learning environment that fosters students’ mathematical growth and prepares them for success in future math courses and careers.
Curriculum Design for Integrated Math 2
Curriculum design for Integrated Math 2 involves creating a comprehensive and cohesive learning experience that integrates concepts from algebra, geometry, statistics, and probability.
Principles of Curriculum Design
The principles of curriculum design for Integrated Math 2 include:
- Alignment with Standards:The curriculum should align with state and national standards for mathematics education.
- Coherence:The curriculum should be organized in a logical and sequential manner, with clear connections between topics.
- Engagement:The curriculum should be designed to actively engage students in learning through hands-on activities, problem-solving, and real-world applications.
- Rigor:The curriculum should be challenging and provide opportunities for students to develop critical thinking skills and problem-solving abilities.
Developing a Coherent and Engaging Curriculum
To develop a coherent and engaging Integrated Math 2 curriculum, consider the following:
- Start with Big Ideas:Organize the curriculum around key mathematical concepts, known as “big ideas,” that connect different strands of mathematics.
- Use Interdisciplinary Connections:Integrate concepts from other disciplines, such as science, technology, and social studies, to make learning more meaningful.
- Incorporate Technology:Utilize technology to enhance student learning, such as interactive simulations, data analysis software, and graphing calculators.
- Provide Opportunities for Hands-On Learning:Engage students in hands-on activities, such as building models, conducting experiments, and solving real-world problems.
Examples of Well-Designed Integrated Math 2 Curricula
Some examples of well-designed Integrated Math 2 curricula include:
- Integrated Math 2: College Board
- Integrated Math 2: EngageNY
- Integrated Math 2: Pearson
These curricula are designed to align with standards, provide coherent and engaging learning experiences, and incorporate technology and hands-on activities.
Common Challenges in Teaching Integrated Math 2
Integrated Math 2 presents unique challenges for teachers due to its interdisciplinary nature and emphasis on real-world applications. Overcoming these challenges requires a combination of pedagogical expertise and a deep understanding of the subject matter.
Student Learning Difficulties
Students may struggle with the abstract concepts and complex problem-solving tasks in Integrated Math 2. To address this, teachers can:
- Break down complex concepts into smaller, manageable chunks.
- Provide concrete examples and real-world applications to make abstract ideas more relatable.
- Use visual aids, manipulatives, and technology to enhance understanding.
Assessment
Assessing student learning in Integrated Math 2 can be challenging due to the variety of skills and knowledge required. Teachers can overcome this by:
- Using a range of assessment methods, including formative assessments, performance tasks, and standardized tests.
- Developing rubrics that clearly define the criteria for success.
- Providing timely and specific feedback to students on their progress.
Collaboration
Integrated Math 2 often requires collaboration between teachers from different disciplines. To facilitate effective collaboration, teachers can:
- Establish clear roles and responsibilities for each teacher involved.
- Develop shared lesson plans and assessments.
- Meet regularly to discuss student progress and identify areas for improvement.
Resources for Teaching Integrated Math 2
Resources for teaching Integrated Math 2 are readily available, providing support for educators in delivering engaging and effective instruction. These resources encompass a wide range of materials, including textbooks, online platforms, and professional development opportunities.
Textbooks
Textbooks remain a fundamental resource for Integrated Math 2, offering comprehensive coverage of the curriculum. They provide students with structured learning materials, step-by-step explanations, and practice exercises. When selecting a textbook, consider factors such as the alignment with the curriculum, the clarity of presentation, and the availability of supplemental materials.
Online Platforms
Online platforms offer a wealth of resources for teaching Integrated Math 2. These platforms typically provide interactive simulations, videos, games, and assessment tools. They can be used to supplement classroom instruction, provide students with additional practice opportunities, and engage students with the material in a more interactive way.
Professional Development
Professional development opportunities are essential for teachers to stay up-to-date on the latest teaching strategies and resources for Integrated Math 2. These opportunities may include workshops, conferences, and online courses. They provide teachers with the knowledge and skills necessary to effectively implement the curriculum and support student learning.
Top FAQs
What are the key features of Big Ideas Integrated Math 2?
Big Ideas Integrated Math 2 emphasizes mathematical modeling, technology integration, and effective teaching strategies to develop students’ critical thinking and problem-solving skills.
How does Big Ideas Integrated Math 2 prepare students for the real world?
Through real-world examples and applications, Big Ideas Integrated Math 2 helps students understand the relevance of mathematics in their daily lives and future careers.
What are the benefits of using technology in Big Ideas Integrated Math 2?
Technology in Big Ideas Integrated Math 2 enhances student learning and engagement by providing interactive simulations, data analysis tools, and virtual manipulatives.